
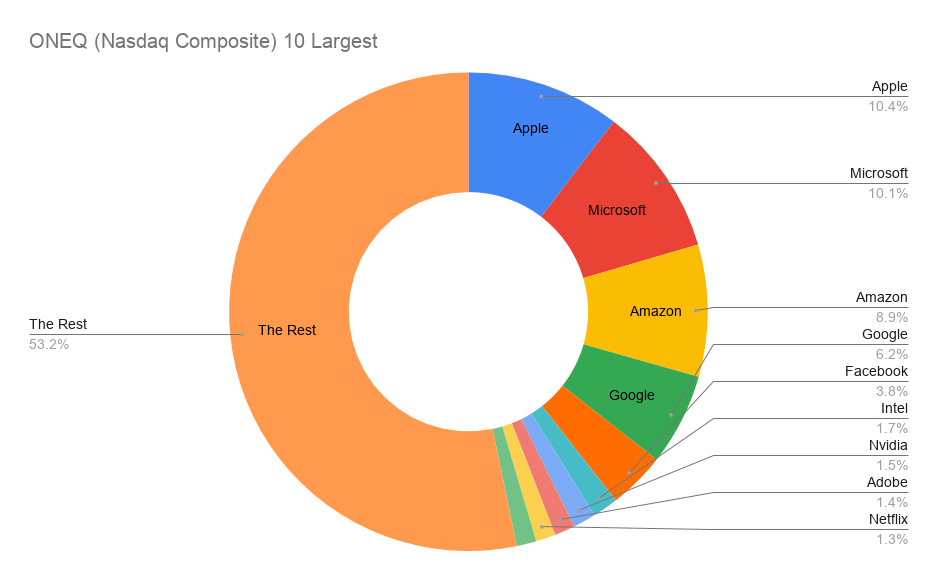
The index is calculated by taking the total value of the weightings of all the stocks on the exchange, multiplied by the closing price of each stock. This means that the largest companies listed on this exchange have the greatest impact on the end value of the index. The NASDAQ Composite is calculated using a market capitalisation-weighted method. The NASDAQ listing qualifications department reviews these companies annually to determine their eligibility for this market. It includes 1,200 US and international stocks. The companies that meet these requirements are mostly large-cap companies. The selected global market has the most stringent requirements in terms of funding, liquidity and corporate governance. This market has 1,450 stocks that are listed in the US and on other international stock exchanges. The global market consists of medium-sized companies, and these companies must meet the NASDAQ's liquidity and funding requirements. It was previously known as the "small cap" market before being renamed the capital market. It is an equity market for companies with a small market capitalisation. The capital market has the least stringent requirements of the three market levels. Stocks listed on the NASDAQ Composite index fall into one of three market categories, based on the listing requirements they meet.

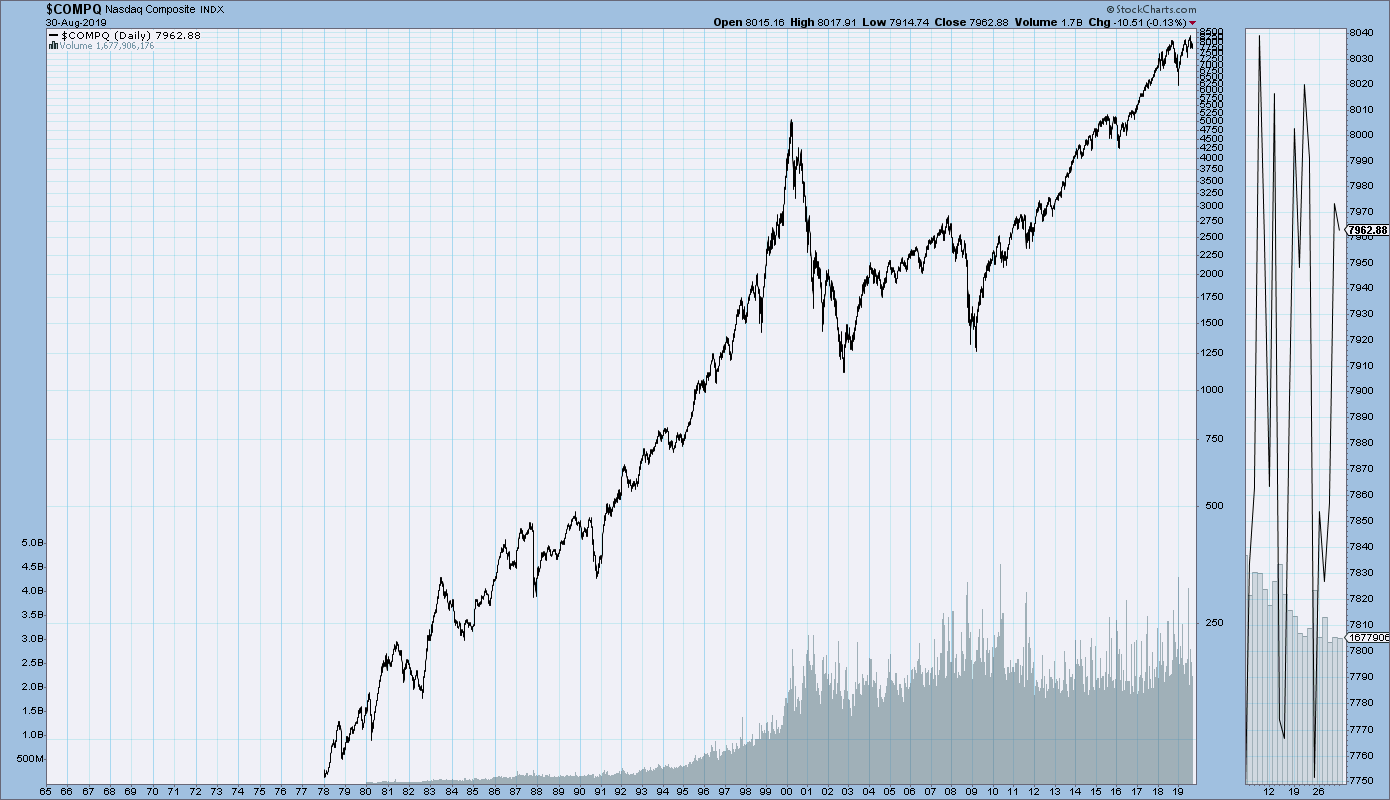
If the stock doesn't meet these requirements, it is ineligible for the NASDAQ Composite and is removed.The security must be one of the following types of securities: American Depository Receipts, common stock, Economic Interest Shares, Real Estate Investment Funds, limited partnerships and Tracking Stock.The only exception to this requirement would be if the security was listed on another US stock exchange before 2004 and is still on it. The security must only be listed on the NASDAQ exchange.NASDAQ Composite inclusion criteriaįor a security to be considered for listing on the NASDAQ Composite, it must meet the following criteria: In April 2015, the index broke a 15-year record of over 5,000 points. Subsequently, the index gradually recovered with the help of the US Federal Reserve's quantitative easing (=printing fake cash) programme. In March 2009, the NASDAQ Composite closed at a low of 1,265.49. In September 2008, the index lost nearly 200 points, dropping below 2,000. In the first quarter of 2007, the index hit an intraday level of 2,862, the highest value since the dot-com bubble collapse. After the crisis, the index gradually recovered until 2007/2008, when the global financial crisis erupted. In April 2000, the index fell to 3,226 and reached its most recent low in October 2002, at 1,108.49. It was followed by a steady increase, peaking at 5,133 in March 2000. In the summer of 1995, the index broke the 1,000-point mark for the first time. The composite index started with 50 companies and a starting value of 100, with the number of companies rising to over 3,500 today and the index reaching a high of 14,095 in February 2021.ĭuring the boom and the dot-com collapse, the NASDAQ Composite posted mixed results between 19. When it was created in New York, the NASDAQ was the world's first electronic exchange, which enabled it to attract new technology companies, such as Microsoft, IBM and Oracle. Since its 1971 launch, the NASDAQ has grown to become the second-largest stock exchange after the NYSE in terms of market capitalisation. The exchange also includes the NASDAQ-100, an index of the largest non-financial companies listed on the NASDAQ stock exchange. The majority of companies listed on the NASDAQ Composite are technology companies, such as Apple, Amazon, Netflix, Dell, Cisco and Oracle. It's one of the most followed US indices, along with the Dow Jones Industrial Average and the S&P 500. The NASDAQ Composite is an index featuring 3,500 common stocks listed on the NASDAQ stock exchange.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
